Cross cut
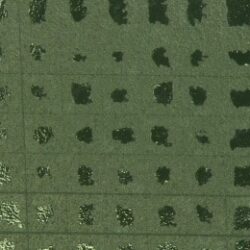
The cross cut is used to determine the adhesive strength or adhesion of coatings on a varnished surface. Six parallel cuts are made with a special cross-cut knife at regular intervals on the coating. Then six further cuts are made at right angles to the resulting cuts on the surface. This creates a uniform square pattern. It is important that all cuts go down to the surface and scratch it without damaging it badly. Afterwards an adhesive tape is stuck on parallel to one direction of the cuts and then removed jerkily at an angle of 60°. The grid is then inspected and evaluated according to its condition. During this process, the grid cut characteristics are rated from 0 (very good) to 5 (very bad), abbreviated Gt 0 to Gt 5.
Relating to plasma, the cross cut is used to compare and evaluate the adhesive strength before and after plasma treatment. The example below shows a test with test printed circuit boards with poor adhesion properties. Here the left PCB was treated with plasma before soldering and painting, the right PCB shows the result without previous plasma treatment. By plasma treatment a surface energy of >44 mN/m could be achieved, whereas the surface energy without plasma treatment is only 32-34 mN/m.
Thus, the cross cut clearly provides proof of the improvement of the adhesion of the paint by previous plasma treatment.
Learn about our products >>