Hydrophobic recovery
Hydrophobic recovery describes the decrease in plasma activation with time: If plasma treated surfaces are not directly subjected to an adhesive follow-up process such as gluing, painting or printing, a decrease in the surface energy, initially enhanced by the plasma, can be observed over time.
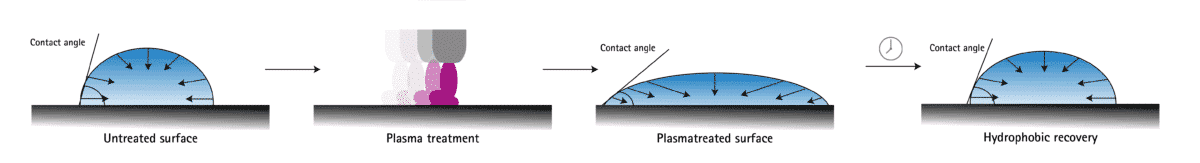
This effect typically occurs after a few hours or days and depends on the material and external conditions such as humidity, temperature or friction. With special plastics such as some silicones, the decrease in plasma activation can occur after only a few minutes. Therefore, it is usually not recommended to store plasma-treated components. Instead the activated surfaces should be processed as soon as possible, which also prevents contamination through transport or storage.
The most important factor is the material used for bonding. Depending on the time of the activation decline, the plastics can be divided into four groups, which are shown in Table 1.
| Hours | Days | Weeks | Months |
|---|---|---|---|
| TPU | PP | LDPE | HDPE |
| PDMS | PCL | SU-8 (Epoxy) | PS |
| PMMA | PBT | PEEK | PC |
| ABS | |||
| PUR | |||
| PES |
In addition to the influence of the material, the following factors also play an important role:
- Influence of the activation method
- Evaluation of the activation decline
- Mechanisms of the decline of activation
- Influence of thermal load